Introduction
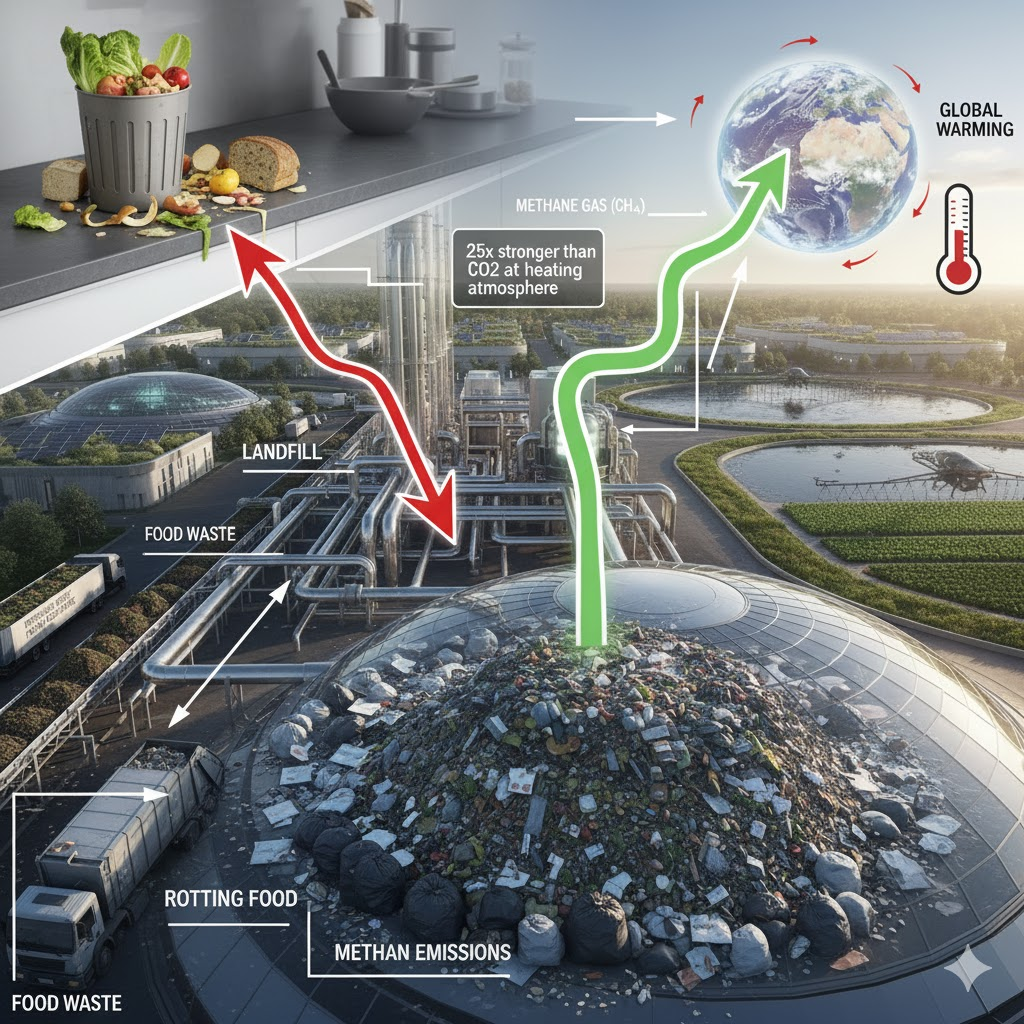
Approximately 1.05 billion tonnes of food are wasted each year globally. The food that people are wasting does not go away, but instead is being dumped and sitting in landfills. That food is rotting and creating problems in the environment. It creates methane, which is a greenhouse gas that is 25 times as strong as carbon dioxide at heating the atmosphere, contributing to global warming. In addition to that, a more scary statistic is that researchers and scientists have found that for every kilogram of food protein wasted, 15 to 750 kilograms of CO₂ are emitted into the environment each year (ACS Chemical Reviews, 2022). With this, global warming is rapidly increasing, and resources are becoming more scarce and harder to get. This poses the question of what the solution to the problem would be. Scientists, researchers, and developers are constantly looking for new ways to solve this problem, in hopes of reducing waste and producing cleaner and more efficient energy. Currently, according to the USDA, between 30-40% of America’s total food supply is lost to landfills. This then amounts to roughly 133 billion pounds and more than $160 billion worth of food annually. Researchers have developed the knowledge to find that solutions lie in the ability to turn food waste into renewable energy. Turning food waste into energy would have a huge impact on the environment as it would get rid of landfill waste, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and provide a cleaner source of energy. It would have a massive impact on the environment. Utilising food waste would be another great source of sustainable energy for the world, as it would help clean up the environment and make it safer and cleaner. However, like any other solution to a problem that may seem all good, they always have some sort of challenge that could arise and make it much more difficult. Some examples of challenges are pollution, like transportation, and chemical imbalance; these examples can be very costly to implement, and could also hurt the environment. This essay will outline the various benefits of turning food waste into energy, as well as the impacts it may have on the environment, technologies present, and possible conflicts that may arise. To ultimately answer the question of whether or not turning food waste into energy is a successful solution or an environmental problem. The first topic that will be introduced is that of the benefits of turning food waste into energy.
Benefits of food waste

https://blog.anaerobic-digestion.com/converting-food-waste-into-energy-at-home-techniques-tips/
Turning food waste into energy has economic and environmental advantages. The biggest advantage is that the amount of waste entering landfills will be greatly reduced. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP, n.d.) estimates that food waste accounts for more than 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions. When food decomposes in landfills, it produces methane, but when that food decomposes and is handled properly with regulated systems, that same gas that can harm the environment is captured and turned into renewable energy. Not only does this reduce dangerous emissions, but it also replaces fossil fuels with a cleaner source of energy, and the CS Chemical Reviews (2022) paper, “Turning Food Protein Waste into Sustainable Technologies”, informs that food protein waste may be used to produce value-added compounds and bioenergy, thereby creating economic and environmental value. In doing this, the people can now create renewable natural gas, electricity, and even fertiliser for the soil. The United Nations reinforces that countries utilising food waste in fertiliser and biogas are exceeding climate goals as well as energy goals. The combination of these systems shows an increase in a strong economy, where waste is not just thrown away but is being recycled into something useful. The circle of waste suggests sustainability since it prevents the cycle of waste, where that waste becomes a resource and not a problem for the environment. In addition to preventing climate change and reducing global warming, it also saves money by reducing landfill space and producing cheaper energy.
How turning food waste into energy benefits the community
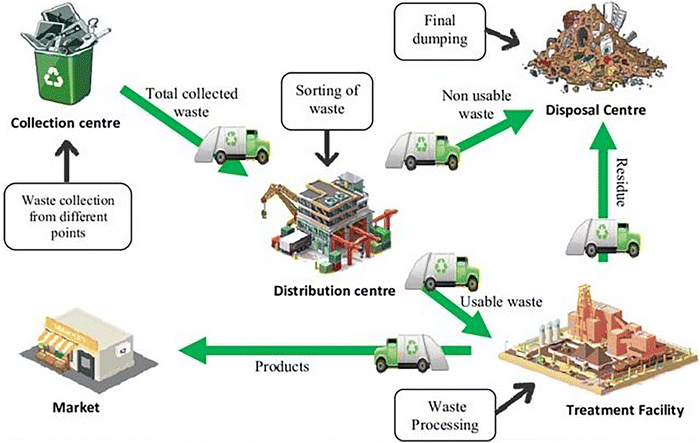
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2025/ma/d5ma00449g
Turning food waste into energy does not just protect and clean up the environment, but it can also help people and communities in very beneficial ways. When cities and towns begin collecting and recycling food waste and using it, and then turning it into energy, this type of work would provide new and more opportunities for people who may be in need and for people who may not have access to a good education. These jobs would include collecting food waste, sorting it, and then operating and maintaining the energy plants where the food waste would be turned into energy. In addition to this, research has shown that turning food waste into energy can help the local economy by keeping money coming and flowing within the community instead of paying taxes for imported fossil fuels. When countries depend less on fossil fuels like oil and gas imports, they will save money and have more control over their energy supply. Turning food waste into energy helps protect them from sudden price increases that are caused by world events like wars and shortages of resources.
Benefits of food waste for farming

Programs and systems that turn food waste into energy can, in fact, benefit farmers and local food producers. For example, after the food waste is turned into energy, the leftover materials can be turned into fertiliser for plants and crops, which would improve soil health and help with the growth process for crops. This now means that farmers can spend less money on chemicals and fertilisers, as they can use food waste as fertiliser, and this will also allow them to produce food more efficiently. Countries like Sweden and Germany have already begun doing this, utilising food waste to produce biogas and fertilisers, and have reported that their farmers have saved a significant amount of money, while also improving air quality. As we discussed earlier, these programs help reduce landfill waste, which costs the government millions of dollars each year to maintain and expand. This example is another reason why turning food waste into energy is a solution to one of the government’s problems and saves the government money. Now that money can go to other important things rather than land on landfill maintenance.
Trust in the tech
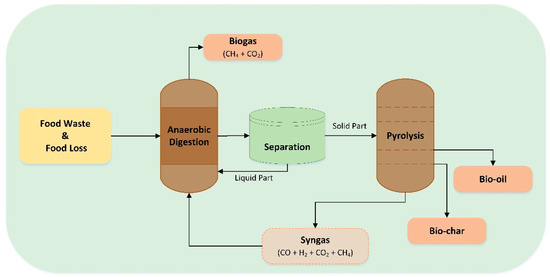
The future of turning food waste into energy technology looks very trustworthy and promising, especially as technology and innovations become more advanced and government policies begin to make that process that much easier. Scientists around the world are now developing advanced methods like hydrothermal liquefaction, where food waste turns into liquid fuel, and gasification, which turns waste into gas using heat and pressure. These are two innovations that food waste contributes to. These technologies are still in the testing phase, but if passed, they could make turning food waste into energy that much easier, faster, and cleaner. For example, researchers in Japan and South Korea are now working on new ways to combine different types of organic waste to increase the amount of energy being produced while lowering greenhouse gas emissions at the same time. Along with new technology, as well as a strong government, rules and regulations, and community education are key things to making these systems work in the long run. Many different experts argue that turning food waste into energy programs should definitely be a part of a larger plan that also includes reducing food waste, composting, and recycling. This approach would create a strong economy where waste is reused instead of being thrown away to sit and rot in a landfill. Governments can encourage people and businesses to participate by proposing tax breaks and financial awards for helping out with recycling food waste properly. Some cities in Europe and Asia now give discounts to people who collect waste and separate waste correctly. These programs can show people that there are benefits to changing their habits in life.
The importance of governmental and social collaboration in turning food waste into energy

However, for all of these types of programs to end up succeeding, communities need good funding, training, as well as the public to participate and do their part. If people do not sort their waste properly and local governments do not provide enough places to collect the food waste, then the systems will not work as they are supposed to. Studies show that when communities are educated about how to separate and organise food waste from other garbage, the quality of that community’s energy production improves. significantly as containment problems that other communities face decline. This means that turning food waste into energy is not just a technological problem, but it is also a social problem. Governments, schools, and organisations must work together, and if they do that, it would make it easier on everyone and allow everyone to participate to make it a success. With the right structure and a strong community effort, this process can lead to great things like a cleaner environment, more stable energy supplies, and a stronger economy in the end. Public collaboration with food waste collection and recycling is a must for the system to be actually effective. The EPA (n.d.) cites that public and commercial sectors need to sort the waste properly and support local sustainability initiatives. What this is trying to say is that technology does do a lot, but it alone is not enough. Many other factors go into this system for it to run smoothly and be successful, like how to implement it, regulations, and public engagement.
Challenges and environmental risks

https://www.epa.gov/sustainable-management-food
This passage will explain different environmental and social risks with the idea of turning food waste into energy. Even though turning food waste into energy has many benefits, there will always be risks, and just like any invention or solution, there are always challenges and problems that have to be figured out. The process has included environmental and operational risks that need to be figured out and handled properly. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA, n.d.) realises that among the main issues is with human actions incorrect sorting of waste. The majority of food waste in the United States is indeed contaminated with plastics, metals, and even chemicals; therefore, it becomes a big problem and an even riskier way to produce energy. This could turn into a very big problematic situation. A lot of contamination results in faulty equipment, poisonous emissions, and even soil pollution when food waste is used as fertiliser. There is another problem, as in Policastro and Fabbricino (2023), where anaerobic digestion has the potential to provoke microbial imbalance if not well regulated. Microbial imbalances let out unwanted toxins and gases that can kill soil and water quality. The study also talks about how certain chemical traces in food waste, such as preservatives and cleaning products, remain present after digestion and infect the by-products.
The expensive aspects of turning waste into energy
In addition to this, large facilities can have an environmental cost to them. They use insane amounts of energy to operate, and mishandling of the biogas can result in methane emissions, which is a very effective greenhouse gas. Their production and maintenance are also very expensive and pricey, making them inaccessible to developing countries that could most definitely utilise waste-to-energy technology.
How transportation can cause a problem

One of the biggest problems that does not seem like a problem is the transportation of food waste. Trucks that move a large amount of food waste from homes, restaurants, and even businesses to processing plants use a lot of fuel, and within that, there are a lot of carbon emissions that are being released into the atmosphere. Now, if these trucks travel long distances, the emissions could potentially cancel out some of these environmental benefits that would be gained from energy production because of the pollution they are creating. It is almost like on one hand it is good because it’s cleaning the environment and creating energy, but then on the other hand it’s contributing to global warming and pollution through the trucks. A solution to this problem that experts suggest is that they should have smaller local processing centers so that food waste does not have to travel that far, and fewer emissions are released into the air. This is a great idea that would allow for a cleaner system and more efficient, but again, it requires more money and planning with the government.
Challenges with the process of cleaning the waste before it is turned into energy
In addition to this, another challenge that comes with this system and program comes from the process of cleaning and preparing the food waste before it is ready to be used as energy. A lot of food waste often contains plastics, metals, and chemicals from things like packages and cleaning products. These contaminations must be removed before being processed, which tackles time and money as well and energy. If these things are not removed properly, then they can damage machinery and, worse, can release toxic chemicals into the air and the soil. Even after processing, the leftover materials, also known as digestate, can still contain very small amounts of dangerous substances. If this digester is used as fertilizer and is contaminated, dirt can harm the soil and pollute water systems as well. Researchers say that heavy metals, preservatives, and other chemicals from water could harm the environment if not handled with care. Energy production facilities by themselves can use a lot of energy and resources as well. Some of these plants require a really high amount of heat and electricity to run. Most of that energy comes from fossil fuels, and the process becomes less sustainable. It is very important to consider the cost of buildings and the maintenance of these facilities. Developing countries that face food waste problems may not have the resources or money to build these facilities, which means that they could potentially be left out of the benefits that food waste brings.
How order and noise pollution cause a problem
Another challenge is the odor and noise pollution that the energy plants create, and this could negatively affect nearby residents. To fix this problem, the governments and the companies of these plants would need to follow strict regulations and environmental guidelines. There will always be a problem that needs to be solved, and although turning food waste into energy has many benefits, it will not be perfect. Each stage, from collecting to transporting the waste to processing it and using it, will never be perfect, and to make it as perfect as possible, it needs to be done properly and handled well. Researchers and experts on this have agreed that this needs to be tested and managed by tracking the rules of the program to see if it really is making an environmental impact. It definitely is in the air to be a great solution to a big worldwide problem, and with these challenges, it still has the potential to be a big success.
Conclusion
Overall, turning food waste into clean energy, renewable energy, is one of the best ways to create a successful future that thrives. It addresses various world issues at once, like climate change, energy shortages, and too much waste in landfills. As shown by research such as UNEP (n.d.) and research by ACS Chemical Reviews (2022), the utilization of food waste as a resource can decrease emissions by a significant amount and construct a strong economy. In addition, you have technologies such as anaerobic digestion and gas conversion, which then offer new ways of turning food waste into power, heat, and fuel. This, however, comes with problems that need to be addressed. Policastro and Fabbricino (2023) and EPA (n.d.) argue that food waste, if not sorted properly and handled well, could lead to contamination in the environment, soil degradation, and inefficiencies. It also requires very detailed policies, technological regulations, and societal participation to be a complete success. Finally, the question that is trying to be answered is can turning food waste into energy can be beneficial or problematic to the environment? Ultimately, Society holds the answer. If done responsibly and well, and handled properly, with careful observation and oversight, good segregation, and global cooperation, it can turn one of the environment’s biggest conflicts and challenges into a renewable energy resource. Although if it is done poorly, it can be yet another source of environmental pollution and damage the earth, rather than solving a problem and making it better. It is not technological success but responsibility, and the food waste is no longer garbage but a resource for a cleaner future.
References
ACS Chemical Reviews. (2022). Turning food protein waste into sustainable technologies. American Chemical Society.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00236
Argonne National Laboratory. (2017). Waste-to-fuel: A case study of converting food waste to renewable natural gas as a transportation fuel. https://www.osti.gov/biblio/1392468
Massachusetts Department of Energy. (n.d.). Anaerobic digestion case studies. https://www.mass.gov/info-details/anaerobic-digestion-case-studies
Policastro, G., & Fabbricino, M. (2023). Anaerobic digestion of food waste: New research, challenges, and opportunities. Fermentation, 9(5), 473. https://www.mdpi.com/2311-5637/9/5/473
Ren, J., et al. (2018). A comprehensive review on food waste anaerobic digestion: Research updates and tendencies. Bioresource Technology. https://tohoku.elsevierpure.com/en/publications/a-comprehensive-review-on-food-waste-anaerobic-digestion-research
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). (n.d.). Turning waste into energy. https://www.unep.org/
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). (n.d.). Sustainable management of food. https://www.epa.gov/sustainable-management-food
Economou, F. (2024). Turning Food Loss and Food Waste into Watts: A Review of Technologies and Environmental Benefits. Energies, 17(13).https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/17/13/3191?
Roy, P. (2023). A Review on the Challenges and Choices for Food Waste Valorization and Energy Recovery. ACS Environmental Au.https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsenvironau.2c00050?
Siva Raman, S., & Stringer, L. C. (2024). Challenges and Solutions for Food Waste‐Based Biogas Production for Energy Generation in Malaysia: A Review. Journal of Wastes and Biomass Management, 6(1), 47‐56.https://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/id/eprint/215866/1/1jwbm2024-47-56.pdf?
Mir, M. A., Chang, S. K., & Hefni, D. (2024). A Comprehensive Review on Challenges and Choices of Food Waste in Saudi Arabia: Exploring Environmental and Economic Impacts. Environmental Systems Research, 13(40).https://environmentalsystemsresearch.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40068-024-00364-5?Soni, A. (2025). Waste‐to‐Energy Technologies: A Sustainable Pathway for Waste Management and Energy Recovery.Materials Advances, [pre‐publication].https://pubs.rsc.org